Bank guarantee what is it
Hello everyone. At work I was in a cool restaurant yesterday - the client made an appointment there.
After a rather hearty dinner, he explained his situation.
He is planning a major deal, but the other side requires the most reliable collateral. She offered him an option with a bank guarantee - she told what these were and what were the main features.
This was fine with him, after which we moved to continue the meeting in karaoke. A couple of days later, I wanted to tell you all the details about this type of guarantee. Go.
Bank guarantees
A bank guarantee is one of the ways to ensure the fulfillment of obligations, in which a bank or other credit institution (guarantor) issues, at the request of the debtor (principal), a written obligation to pay the creditor (beneficiary) a sum of money upon submitting a demand for its payment.
The requirements for the guarantee used by the participants in the placement of the State order, and the procedure for its provision and issuance, are established by Federal Law 44-FZ "On the contract system in the procurement of goods, works, services to meet state and municipal needs."
When concluding a State contract for an electronic auction, the winner is obliged to provide a scanned copy of the bank guarantee indicating the essential conditions of the State Contract - the amount of security, validity period, the name of the Customer, the Contractor and the subject of the contract.
This copy is attached as an electronic document through the electronic platform where the auction was held.
The issued bank guarantee is a document that cannot be returned because it was “not needed”. In accordance with the norms of the current legislation, the bank guarantee is terminated under the following conditions:
- upon payment to the beneficiary of the amount for which it was issued;
- upon expiration of the term specified in the guarantee for which it was issued;
- due to the refusal of the beneficiary from his rights under the guarantee and its return to the guarantor;
- a written statement of the beneficiary about the release of the guarantor from his obligations.
The termination of the obligations of the guarantor on the above grounds does not depend on whether the guarantee has been returned to him, the guarantor, who became aware of the termination of the guarantee, must immediately notify the principal of this.
Source: http://gosgarant.ru/bank-guarantees/
How is the BG registration deal going?
A bank guarantee is the assumption by a bank of certain financial obligations under contracts taken by its client.
For the client, the use of a guarantee means the opportunity to participate in large contracts and increase the status as a reliable partner.
This is the definition given by the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. It can be considered basic.
By virtue of a bank guarantee, a bank, another credit institution or an insurance organization (guarantor) give, at the request of another person (the principal), a written obligation to pay the principal's creditor (beneficiary) in accordance with the terms of the obligation given by the guarantor a sum of money upon the submission by the beneficiary of a written demand for its payment.
For final clarity, we will analyze the process of providing BG in more detail.
The general scheme is quite simple:
- A client (individual entrepreneur or legal entity) who plans to conclude a large contract applies to a bank (or several banks) with an application for a guarantee.
- Based on the package of documents, the bank makes a decision on the provision of the service or refusal.
- If the bank has agreed, the client opens a current account in it and pays a commission.
- If the transaction is canceled through the fault of the client (principal) or in other cases when the client has debts under the guaranteed contract, these debts are paid by the bank (of course, within the agreed amount).
In simple words
It is necessary to understand that in order to obtain a BG, the possession of collateral property of the corresponding value is required.
Thus, this service relates not so much to insurance (an insurance contract is something like a bet), but to liquidity management.
The bank, in fact, does not guarantee the client's actual debts, but that it will exchange these debts for his collateral (real estate, equipment), which is not liquid enough to by itself ensure the obligations under the agreement.
Such a service accelerates the turnover of funds, which is beneficial to all participants in the transaction.
Source: http://biznes-kredit.info/bankovskaya-garantiya/sut-chto-eto.html
Letters of credit and guarantees. How it works

The buyer of the goods is interested in buying the goods with a deferred payment, and the seller is interested in maintaining sales markets.
The seller is ready to deliver the goods with a deferred payment (trade credit), but requires additional guarantees of payment. The solution to the issue in this case is the use of a bank guarantee.
After the conclusion of the contract (1), providing for the delivery of goods on terms of subsequent payment, the buyer (principal) applies to the bank (usually the service provider) with a request to provide a bank guarantee of payment and provides the bank with a package of necessary documents (2).
The bank issues a bank guarantee (3) in favor of the seller (beneficiary under the guarantee), containing the bank's obligation to pay the beneficiary a certain amount of money in case the buyer fails to fulfill his obligations to pay for the delivered goods.
The bank guarantee is sent to the beneficiary directly or through his servicing bank.
Attention!
After receiving a bank guarantee, the seller delivers the goods (works, services) (4). Upon the occurrence of the deadlines specified in the contract, the buyer makes payment for the delivered goods.
In case of non-payment, the supplier submits a demand for payment under the guarantee to the guarantor bank, which, after checking the declared demand for compliance with the terms of the guarantee, pays the required amount to the beneficiary (supplier).
In a similar way, other contractual obligations can be provided: for the supply of goods, for the return of an advance payment in case of non-delivery, for warranty service of the supplied equipment, etc.

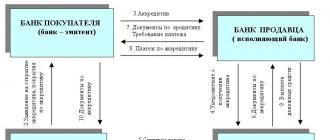
After the conclusion of a contract (1) for the supply of goods (performance of work, provision of services), in which a documentary letter of credit is provided as a form of payment, the buyer (the applicant for the letter of credit) applies to the servicing bank with an application for opening a letter of credit (2).
The main terms of the letter of credit are usually specified in the contract (1).
Simultaneously with the application, the buyer provides the bank with a monetary cover for the amount of the letter of credit (makes a reservation of funds).
If necessary, the buyer can apply to the bank with a request to open a letter of credit with the granting of a deferral to the buyer to transfer the coverage.
When concluding an agreement with a bank for opening such a letter of credit (agreement for opening an uncovered letter of credit), cash coverage is provided to the bank in accordance with the agreed schedule, but no later than the due date for payment under the letter of credit.
After receiving all the necessary documents from the ordering party (buyer) and concluding an agreement, the buyer's bank (issuing bank) opens a letter of credit (3) - sends a message to the seller's bank.
The seller's bank (advising bank) informs the seller (beneficiary) about the opening of the letter of credit (3).
After receiving notification of the opening of a letter of credit, the beneficiary (seller) dispatches the goods (performance of work, provision of services) (4).
To receive payment for the shipped goods, the seller provides a package of documents (5) specified in the letter of credit to the advising bank.
The advising bank, depending on the terms of the letter of credit, may either be authorized to make payment under the letter of credit (5), or must forward the provided documents to the issuing bank.
After checking the documents, the bank makes payment under the letter of credit (6). If the documents are drawn up in violation of the terms of the letter of credit, payment is made with the prior consent of the buyer.
If the provided documents are drawn up in full compliance with the terms of the letter of credit, payment under the letter of credit is made by banks, regardless of the buyer's opinion and the conditions for providing them with monetary cover under the letter of credit.
After the payment is made under the letter of credit, the documents previously received from the seller are transferred to the buyer.
Source: https://cib.com.ua/ru/services/corporate-banking/shemy_garantiy_ru
Bank guarantee as a way to ensure the fulfillment of obligations
A bank guarantee is a way to ensure the fulfillment of the obligations of the company of the supplier of goods or services to the customer.
In Russia, a bank guarantee has not yet found such widespread use as in foreign countries. However, in recent years, the popularity of this type of security for the fulfillment of obligations has been increasing in connection with the use of a bank guarantee to ensure the execution of government contracts.
A bank guarantee is a written obligation of a bank or other credit institution, insurance organization (guarantor) assumed at the request of another person (principal), by virtue of which the guarantor, subject to the conditions stipulated by this obligation and at the request of the creditor of the principal, must pay the latter a certain amount ...
In practice, the term “guarantee” is often used synonymously with “surety”.
However, a bank guarantee differs significantly from all other methods of securing the fulfillment of an obligation.
The similarity between a guarantee and a surety is that both the guarantor and the surety undertake the obligation to pay the sum of money in the event of default by the debtor. The participants in the relationship are also the same.
The peculiarity of a bank guarantee is a one-way transaction. She is self-reliant and independent from the commitment she provides.
Even if the guarantee contains a reference to this obligation (of course, there can be no bank guarantee without the obligation that it provides), the existence of the obligation provided by the bank guarantee to pay a sum of money to the debtor's creditor and its performance are in no way related to the dynamics of the obligation that it is designed to provide.
The guarantor is not released from the performance of his obligations, even if the main obligation has terminated or was invalidated, the bank guarantee continues to be valid.
Attention!
A bank guarantee is characterized by urgency and irrevocability, which means that the guarantor is not entitled unilaterally, i.e. without the consent of the beneficiary, to refuse the assumed obligations.
Revocable guarantees are extremely rare, as they do not correspond to the nature of the bank guarantee and cause distrust on the part of the beneficiaries.
The beneficiary can assign to a third party the right to claim against the guarantor only if the guarantee itself provides for such a possibility.
The bank guarantee is distinguished by a highly formalized relationship. For the issuance of a bank guarantee, the Principal shall pay the guarantor a fee.
Advantages
Despite the fact that for the issuance of bank guarantees is carried out on a reimbursable basis, it is profitable for customers to use it, so a bank guarantee makes it possible to avoid the diversion of funds from circulation. And this is not the only advantage of using it.
Advantages of a bank guarantee for the Borrower:
- a bank guarantee makes it possible to participate in the supply of goods and provision of services for state and municipal customers,
- a bank guarantee makes it possible to obtain a commodity loan from a counterparty, which is secured by a bank guarantee,
- it is possible to defer payment of the amount under the contract for the provision of goods or services for the period for which the guarantee was issued,
- the guarantee fee is usually lower than the interest on the loan,
- there are programs for providing a bank guarantee without additional collateral,
- while simplifying the procedure for issuing a bank guarantee, the difference in the cost of bank services increases.
Advantages of a bank guarantee for the Lender:
- guarantees are more reliable and quickly realizable;
- a bank guarantee allows you to ensure the fulfillment of obligations by the company executing the contract to the customer if the delivery or work is not performed or performed not in the way stipulated in the contract;
- the bank guarantee distributes the risks between the contractor and the customer who signed the contract;
- such a form of securing an obligation stimulates the contractor to accurately and timely fulfill his obligations under the threat of the customer's claims about improper performance of obligations under the state contract;
- the guarantee creates protection of the customer from the risks associated with advance or periodic payments to the contractor;
- the presence of a bank guarantee helps the customer to assess the financial position of the contractor and, as a rule, indicates his ability to fulfill his obligations under the main contract, since the bank's consent to issue a guarantee to the contractor indicates a stable financial position of the supplier.
Objects and subjects
The participants in the relationship with a bank guarantee are:
- Guarantee.
- Principal.
- Beneficiary.
The guarantor can only be a bank, another credit institution, an insurance company.
However, in accordance with the amendments to Federal Law 94-FZ “On Placing Orders for the Supply of Goods, Performing Works, Rendering Services for State and Municipal Needs, which entered into force on August 2, 2010. insurance companies were excluded from the list of organizations that can issue a guarantee to secure a government contract.
A guarantee issued by any other legal entity (commercial or non-commercial), state authority or local government is null and void, i.e., invalid, since all of these entities are not entitled to issue a bank guarantee.
The role of the principal is any person who is the debtor in any obligation. This can be a loan obligation, a sales contract, a lease, etc.
The beneficiary is any person who is the principal's creditor for an obligation secured by a bank guarantee.
The initiative in forming the relationship regarding the bank guarantee belongs to the Principal. At his written request, a guarantee is issued. The position held by the Beneficiary has no legal significance.
Although in practice, the debtor's initiative is dictated by the requirements of the creditor. For example, when concluding a sales contract, which provides for the possibility of payment for goods in installments, the seller may require that the buyer's obligations to pay for the goods are secured by a bank guarantee.
The desire to become a guarantor is expressed by a bank or other credit institution by issuing a corresponding written certificate.
Types of BG
Depending on the purpose of the bank guarantee, there are several types of it.
Bid guarantee or tender guarantee serves to ensure the payment requirements of the party organizing the tender in relation to the party that makes the offer, in the event that the latter either refuses the offer, or cancels the application after the bidding, or refuses to sign the contract or provide additional guarantees for its implementation.
Payment guarantee. This type of guarantee is used to secure the buyer's payment obligations to the seller.
It is applied, as a rule, when settlement occurs upon receipt of goods (services) by the principal or in the case of a commodity loan. Usually, the payment guarantee is unconditional, that is, it provides for payment at the first request of the beneficiary.
Guaranteed customs payments. This type of bank guarantees is issued to importing enterprises so that they can ensure customs payments, be able to pay the costs required by the customs authorities, penalties for loss, damage, the release of goods without the permission of the customs authorities in violation of the established terms of export from the customs warehouse.
Execution guarantee. A performance guarantee is the bank's obligation to pay the buyer the agreed amounts or fines at his request in the event that the seller's obligations under his contractual relationship are not fulfilled or are performed in an inappropriate manner.
Money back guarantee. It represents the obligation of the bank to return the amount of the advance (or its unused part) in the event that the seller does not fulfill his obligations to supply the goods stipulated by the contract.
Loan repayment guarantee. Such a bank guarantee is used to secure credit transactions.
Depending on the terms of payment of the amount of money to the beneficiary, one can distinguish between a guarantee on demand (unconditional) and a conditional guarantee.
In the first case, payment is made at the first written request of the beneficiary, in accordance with the terms of the guarantee.
In the second case, the guarantor must also make payment in accordance with the terms of the guarantee at the written request of the beneficiary, but already accompanied by documents proving or confirming the failure to fulfill (improper fulfillment) by the principal of his obligations.
Bank guarantees are either secured or unsecured. A secured guarantee assumes the presence of a pledge of property or other method of security, while an unsecured guarantee is a simple written commitment from the bank.
Also, guarantees are divided into direct and counter-guarantees. In the first case, the guarantor bank itself assumes the obligation to the beneficiary.
Attention!
A counter-guarantee is issued if the bank, on behalf of the principal, requires the issuance of a guarantee from another bank (including a foreign one) by issuing a counter-obligation.
A confirmed bank guarantee can be confirmed in full or partially by another bank - a confirmed bank guarantee, which is jointly and severally liable to the beneficiary.
Several banks can participate in the issuance of a bank guarantee at once, acting through the main guarantor bank, in this case, a syndicated (consortium) bank guarantee is issued.
Such guarantees are used in large (including international) transactions, and the more banks are involved in issuing a guarantee, the more expensive this service is.
The relationship of the parties when issuing a guarantee
Despite the fact that a bank guarantee is a unilateral transaction and when it is concluded, the will of only one party (the guarantor) is sufficient, the legal connection between the guarantor and the principal has a complex content. Registration of a bank guarantee is carried out in several stages.
The main normative act governing the relationship of the parties is the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. For state or municipal contracts, the requirements for a bank guarantee and the procedure for its provision are established by Federal Law 94-FZ "On placing orders for the supply of goods, performance of work, provision of services for state and municipal needs."
Stages of registration of a guarantee:
- The Principal shall send a written request to the Guarantor to provide a guarantee. Without such a request, the bank guarantee is invalid.
- The guarantor decides on the possibility of issuing a guarantee.
- The Principal and the Guarantor enter into an agreement that will regulate their relationship, determine their rights and obligations.
- The Principal shall pay the Guarantor a fee for issuing the Bank Guarantee.
- The Guarantor issues a bank guarantee to the Principal. It determines the size of the amount for which it is issued, formulates the terms of payment, indicates the period of validity of the guarantee, a list of documents that must be submitted by the Beneficiary along with the demand.
- The Principal transfers the bank guarantee to the Beneficiary. The issued bank guarantee must contain information allowing the beneficiary to verify the following:
- that the guarantee is issued by an entity entitled to this, which should be indicated in its license;
- that the person who signs the document is authorized to perform such actions. In this regard, the beneficiary must either familiarize himself with the guarantor's license, or a certified copy of the license is presented along with the guarantee.
Relationship in the event of the occurrence of the circumstances provided for by the guarantee
In the event of the occurrence of the conditions specified in the agreement, the Beneficiary has the right to demand from the guarantor to pay the amount or part of it in cash.
The claim is presented in writing, with the documents specified in the guarantee attached to it.
It should also be mandatory to indicate how the principal violated his obligations. The beneficiary must complete these actions before the expiration of the bank guarantee.
The guarantor must consider the claim of the beneficiary and the documents attached thereto within a reasonable time.
He is also obliged to exercise reasonable care in order to establish the compliance of this requirement and the accompanying documents with the conditions of the bank guarantee.
When considering the requirements of the beneficiary, the decisive factor is the formal compliance of the requirements of the beneficiary and the documents attached to it with the terms of the bank guarantee, and not ascertaining the guilt of the beneficiary or analyzing the relationship between the beneficiary and the principal.
There are only two possible reasons for the refusal to satisfy the requirement. In the first case, the demand and / or the documents attached to it do not meet the conditions of the guarantee, in the second, the demand and / or the documents attached to it are submitted after the expiry of the period specified by the guarantee.
The guarantor is obliged to immediately notify the beneficiary of the refusal to satisfy his demands, as well as inform the reasons for such a decision.
The guarantor must immediately inform the beneficiary and the principal of the information received by him that the main obligation is either fully or partially fulfilled, or terminated on other grounds, or is invalid; in this case, the amounts stipulated by the guarantee are not transferred to the beneficiary.
But if, after such notification, the beneficiary makes a repeated demand, the guarantor is obliged to satisfy it.
The obligation of the guarantor to the beneficiary is limited to the payment of the amount for which the guarantee was issued.
This is due to the fact that the guarantor fulfills his obligation as a result of the payment to the beneficiary of the amount of money agreed upon by the guarantee. The guarantor is not responsible for losses, does not pay forfeits, etc.
The liability of the guarantor is not limited to the indicated amount in the event that the guarantor does not fulfill the undertaken obligation or performs it in bad faith.
In this case, the beneficiary may incur losses, for example, if the guarantor did not consider his claim within a reasonable time. Therefore, the beneficiary's losses are compensated in excess of the amount for which the bank guarantee was issued.
The guarantor has the right to demand from the principal, by way of recourse, the reimbursement of the amounts that he paid to the beneficiary under the bank guarantee, on the terms determined by the agreement between the guarantor and the principal, and in support of which the guarantee was issued.
The agreement may provide for the principal's obligation to compensate the guarantor for his property losses, both in full and in part.
The same agreement may contain the conditions for the release of the principal from liability, determine the timing of payment by the principal to the guarantor of the corresponding amounts, etc.
Attention!
The principal cannot be required of amounts that are paid by the guarantor to the beneficiary not in accordance with the terms of the guarantee or for violation of his obligations to the beneficiary.
However, according to paragraph 2 of Art. 379 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, such a condition as full or partial compensation of the corresponding expenses of the guarantor may be provided for by a bank guarantee.
Termination of a bank guarantee is made by the beneficiary paying the amount for which the guarantee was issued (due performance of the obligation) or by the end of the period specified in the guarantee.
Also, the guarantee can be terminated by offsetting a counterclaim, the coincidence of the guarantor and the beneficiary in one person, the impossibility of fulfilling the obligation, etc.
According to paragraph 2 of Art. 378 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, the guarantor is obliged to immediately notify the principal of the termination of the bank guarantee.
The beneficiary can waive his rights under the guarantee. In this case, the beneficiary can either return the guarantee, or declare in writing about the release of the guarantor from his obligations.
Source: http://www.souz-finance.com/info/article/articl1.html
What is a bank guarantee - in simple words
A bank guarantee is a document confirming the bank's guarantee to the customer. Its presence confirms that the contractor will fulfill the contract, otherwise the bank will reimburse all losses to the customer.
Advantages
The contractor can be sure that in case of non-payment for the work performed by the customer, the work performed will be paid by the bank under a bank guarantee.
For the Customer, the guarantee is beneficial for its low cost and the ability to pay off the contractor in case of unforeseen circumstances.
The guarantee is a very flexible and convenient financing tool: if an agreement is reached with the seller on the use of the guarantee and the buyer is granted a deferred payment, then the buyer can independently plan purchases and settlements with the seller, provided that the amount of the buyer's debt to the seller does not exceed the amount of the bank guarantee.
The advantage of a bank guarantee is that it helps to avoid various risks, even if a certain commission is paid.
There are different pros and cons of a bank guarantee for different parties to a transaction.
Benefits of a bank guarantee for a borrower organization:
- Upon receipt of a bank guarantee, it becomes possible to supply goods and services to government customers;
- Upon receipt of a bank guarantee, it becomes possible to obtain a commercial loan, which the bank guarantee provides;
- Upon receipt of a bank guarantee, it becomes possible to receive a deferral of payments under the concluded contract for the goods and services provided during the period of the guarantee;
- The commission for the provided guarantee is usually lower than the established bank interest on a commercial loan;
- Regular customers can be provided with a bank guarantee without collateral, according to certain programs;
- When you receive a bank guarantee in a simplified way, the difference in payment for the services performed increases.
Benefits of a bank guarantee for organizing a lender:
- The issued bank guarantees are highly reliable and quick to implement;
- The issued bank guarantee ensures the fulfillment of obligations by the executing organization of the concluded agreement to the customer, if the necessary deliveries of goods or work have not been performed properly;
- The issued bank guarantee redistributes all kinds of risks between the organizations of the customer and the contractor;
- The issued bank guarantee is a powerful incentive for the accurate and proper fulfillment of all contractual conditions under the concluded contract, due to the fact that claims may be made by the organization - the customer about the unfair fulfillment of the contractual conditions;
- The issued guarantee provides the customer with a kind of protection against various risks that are associated with advance payments to the executing organization;
- The bank guarantee makes it possible to assess the financial condition of the executing organization, in order to identify the ability to fulfill the assigned obligations, since the credit institution issues a guarantee only to organizations with a stable financial position.
disadvantages
You have to pay for the registration of the guarantee. Financial institutions will not provide such services for free. And although the cost of opening and maintaining a bank guarantee is less than the interest on a loan, the principal still bears additional costs.
The bank must pay compensation on the basis of one claim of the creditor, having carried out only a formal check of the submitted documents for compliance with the terms of the guarantee agreement.
The bank guarantee does not expire with the fulfillment of the basic obligation.
There is a risk for the lender of the principal obligation of revocation of the license from the issuing financial institution.
And if the sequence of actions in this case is not spelled out in the guarantee agreement itself, the security may simply cease to operate.
There are many models of bank guarantees, so the parties can choose exactly the one that best suits the interests of each.
Since advantages for one side often translate into disadvantages for the other, it is worth looking for a balance point where both parties can mutually cooperate.
Terms of issue and validity
The guarantee is issued by the bank (issuing bank) for a specified period, which can be extended by order of the principal.
The term for issuing a bank guarantee varies depending on the type of bank guarantee and its amount. Bank guarantees in the amount of up to 30 million rubles often fall under express issuance schemes.
Attention!
Banks and brokers offer issuance of such guarantees in 1-3 days. The VBC Online Service offers the issue of an Express Bank Guarantee in 1 hour. If the amount of the bank guarantee is from 30 million rubles, the term of issue at the bank is from 1 to 5 days.
All bank guarantees are perpetual and do not have a definitive expiration date.
Views
There are various types of guarantees: a guarantee of payment, a guarantee of fulfillment of obligations, a guarantee of the return of an advance payment, a guarantee for participation in a tender, etc.
Bank guarantee of payment - the bank provides a guarantee for the payment of the amount specified in the contract or agreement in favor of the seller or executor.
Tender bank guarantee (Guarantee for securing the application) - a document issued by the bank for the payment of the amount in favor of the tender participant. If the contractor refuses to fulfill obligations or the contract is not signed on time.
Bank guarantee of fulfillment of obligations - when the bank undertakes, for example, in the case of an appropriate application from the seller in favor of the buyer, to pay a specific amount of money if the seller does not fulfill its obligations.
Bank guarantee of the return of the advance payment - in this case, the bank's obligation is to pay the amount of the advance in favor of the buyer, if the principal did not fulfill the obligations taken in accordance with the conditions contained in the agreement.
Bank guarantees in favor of the customs and tax services - in accordance with the departmental Order of December 7, 2007 No. 1281, the Russian Federal Customs Service can and must accept financial security for the corresponding payments.
Such a guarantee is provided by banks and insurance companies that are mandatory in the special Register of the Federal Customs Service of the Russian Federation (that is, trustworthy).
Bank guarantees for travel operators - strict requirements are imposed on travel companies when they receive a license, and the presence of bank guarantees for transactions is one of them.
According to the peculiarities of payments to the contractor, there are two main types of bank guarantees: unconditional (on demand) and conditional.
A conditional bank guarantee is a bank's obligation to non-payment of a set amount to the executor of the order, but only subject to the provision of documents evidencing non-payment by the customer.
Unconditional bank guarantee - implies payment by the guarantor bank at the first request of the beneficiary (in writing) without any additional conditions.
All guarantees are secured and unsecured.
A secured bank guarantee requires a certain amount of collateral to act as security.
Any property owned by the customer can be a pledge: real estate, goods in circulation, equipment, securities, etc.
An unsecured bank guarantee of a bank assumes the absence of collateral and is issued on the basis of a written commitment from the bank.
A reliable bank guarantee has such principles as urgent and irrevocable. Under these characteristics, it is assumed that the bank does not have the right to unilaterally refuse to pay money to the contractor.
There are also other types of bank guarantees, for example, a syndicated bank guarantee. This bank guarantee is issued by several banks at once, which operate through one bank.
A syndicated guarantee is usually issued for large transactions, domestic and international. Its cost depends on the number of financial institutions that take part in this transaction.
In addition, there are also direct guarantees and counter-guarantees. A direct guarantee implies that the payment of the obligations will be made by the bank itself.
A counter-guarantee assumes that the bank that issued it can demand a counter payment for obligations from a third-party bank, which is also a party to the transaction.
How to get the?
There are several ways to get a bank guarantee, we will try to briefly explain the advantages and disadvantages of each of them.
- Bank. The longest way is to contact the bank directly, choose the most suitable of all banks that provide BG, collect all the documents yourself (see the list here), and wait for the bank to give an answer.
- Broker. This method is simpler, but it may require paying a fee to the broker. But you do not have to collect all the documents yourself. The broker will do this for you, and will also submit applications to various banks after which you can choose the most suitable one, ready to issue a guarantee according to your conditions.
- Automated Online Service VBC. The easiest way to get a bank guarantee. A personal manager will help you collect all the necessary documents, as well as submit them to all partner banks in a couple of clicks. You just have to choose the most convenient and suitable offer for you.